Wie groß sind
c(H+), c(OH-) und
pOH für eine
Salzsäure mit der
Konzentration
c = 0,03 mol/L?
Lösung:
Salzsäure ist eine starke Säure und dissoziiert in
wäßriger Lösung vollständig.
pH = -log c(HCl) = -log 0,03 mol/L = 1,5
KW = c(H+) · c(OH-) =
1·10-14 mol2/L2
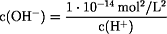
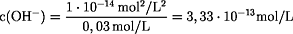
p(OH) = -log c(OH-) = -log 3,33·10-13 mol/L
=12,5
oder einfacher und schneller:
pH = -log c(HCl) = -log 0,03 mol/L = 1,5
pH + pOH = 14
pOH = 14 - pH = 14 - 1,5 = 12,5